Cryptography is both beautiful and terrifying. Perhaps a bit like your ex-wife. Despite this, it represents a vital component of day-to-day internet security; without it, our secrets kept in the digital world would be exposed to everyone, even your employer. I doubt you’d want information regarding your sexual preferences to be displayed to the regional sales manager while at an interview with Goldman Sachs, right?
Computers are designed to do exactly what we ask them to do. But sometimes there are certain things that we don’t want them to do, like expose your data through some kind of backdoor. This is where cryptography comes into play. It transforms useful data into something that can’t be understood without the proper credentials.
Let’s take a look at an example. Most internet services need to store their users’ password data on their own servers. But they can’t store the exact values that people input on their devices because, in the event of a data breach, malevolent intruders would effectively gain access to a simple spreadsheet of all usernames and passwords.
This is where ‘Hash’ and ‘Salt’ help us a lot. Throughout this article, we’re going to explain these two important encryption concepts through simple functions in Node.JS.
What is a ‘hash’?
A ‘hash’ literally means something that has been chopped and mixed, and originally was used to describe a kind of food. Now, chopping and mixing are exactly what the hash function does! You start with some data, you pass it through a hash function where it gets whisked and chopped, and then you watch it get transformed into a fixed-length value (which at first sight seems pretty meaningless). The important nuance here is that, contrary to cooking, an input always produces a corresponding output. For the purposes of cryptography, such a hash function should be easily computable and all values should be unique. It should work in a similar way to mashing potatoes – mashing is a one-way process; the raw potato may not be restored once it has been mashed. Indeed, the result of a hash function should be impenetrable to computer-led reverse engineering efforts.
These properties come in handy when you’re looking to store user passwords on a database – you don’t want anyone to know their real values.
Let’s implement a hash in Node.JS!
First, let’s import the createHash function from the built-in ‘crypto’ module:
const { createHash } = require ('crypto');Next, we ought to define the module that we’re naming as the ‘hash’ (which takes a string as the input, and returns a hash as the output):
function hash(input) {
return createHash();
}We also need to specify the hashing algorithm that we want to use. In our case, it will be SHA256. SHA stands for Secure Hash Algorithm and it returns a 256-bit digest (output). It is important to architect your code so it is easy to switch between algorithms because at some point in time they won’t be secure anymore. Remember, cryptography is always evolving.
function hash(input) {
return createHash('sha256');
}Once we call our hashing function, we may call ‘update’ with the input value and return the output by calling ‘digest’. We should also specify the format of the output (e.g. hex). In our case, we’ll go with Base64.
function hash(input) {
return createHash('sha256').update(input).digest('base64');
}Now that we have our hash function, we can provide some input, and console log the result.
let youShallNotPassPass = 'admin1234';
const hashRes1 = hash(youShallNotPassPass);
console.log(hashRes1)Here’s our baby hash:
rJaJ4ickJwheNbnT4+I+2IyzQ0gotDuG/AWWytTG4nA=
So, how can we use this long, convoluted string of numbers, letters, and symbols? Well, now it’s easy to compare two values while operating with only hashes.
let youShallNotPassPass = 'admin1234';
const hashRes1 = hash(youShallNotPassPass);
const hashRes2 = hash(youShallNotPassPass);
const isThereMatch = hashRes1 === hashRes2;
console.log(isThereMatch ? 'hashes match' : 'hashes do not match’)As long as hash values are unique object representations, they can be useful for object identification. For example, they might be used to iterate through objects in an array or find a specific one in the database.
But we have a problem. Hash functions are very predictable. On top of that, people don’t use strong passwords that often, so the hacker may just compare the hashes on a database with a precomputed spreadsheet of the most common passwords. If the values match – the password is compromised.
Because of this, it’s insufficient to just use a hash function to store unique ids on a password database.
And that’s where our second topic makes an entrance – Salt.
‘Salt’ is a bit like the mineral salt that you would add to a batch of mashed potatoes – the taste will definitely depend on the amount and type of salt used. This is exactly what salt in cryptography is – random data that is used as an additional input to a hash function. Its use makes it much harder to guess what exact data stands behind a certain hash.
So, let’s salt our hash function!
First, we ought to import ‘Scrypt' and ‘RandomBytes’ from the ‘crypto’ module:
const { scryptSync, randomBytes } = require('crypto');Next, let’s implement signup and login functions that take ‘nickname’ and ‘password’ as their inputs:
function signup(nickname, password) { }
function login(nickname, password) { }When the user signs up, we will generate a salt, which is a random Base64 string:
const salt = randomBytes(16).toString('base64');And now, we hash the password with a 'pinch' of salt and a key length, which is usually 64:
const hashedPassword = scryptSync(password, salt, 64).toString('base64');We use ‘Scrypt’ because it’s designed to be expensive computationally and memory-wise in order to make brute-force attacks unrewarding. It’s also used as proof of work in cryptocurrency mining.
Now that we have hashed the password, we need to store the accompanying salt in our database. We can do this by appending it to the hashed password with a semicolon as a separator:
const user = { nickname, password: salt + ':' + hashedPassword}Here’s our final signup function:
function signup(nickname, password) {
const salt = randomBytes(16).toString('base64');
const hashedPassword = scryptSync(password, salt, 64).toString('base64');
const user = { nickname, password: salt + ':' + hashedPassword};
users.push(user);
return user;
}Now let’s create our login function. When the user wants to log in, we can grab the salt from our database to recreate the original hash:
const user = users.find(v => v.nickname === nickname);
const [salt, key] = user.password.split(':');
const hash = scryptSync(password, salt, 64);After that, we simply check whether the result matches the hash in our database. If it does, the login is successful:
const match = hash === key;
return match;Here is the complete login function:
function login(nickname, password) {
const user = users.find(v => v.nickname === nickname);
const [salt, key] = user.password.split(':');
const hash = scryptSync(password, salt, 64).toString('base64');
const match = hash === key;
return match;
}Let’s do some testing:
//We register the user:
const user = signup('Amy', '1234');
//We try to login with the wrong pass:
let isSuccess = login('Amy', '12345');
console.log(isSuccess ? 'Login success' : 'Wrong password!')
//Wrong password!
//We try to login with the correct pass:
isSuccess = login('Amy', '1234')
console.log(isSuccess ? 'Login success' : 'Wrong password!')
//Login successOur example, hopefully, has provided you with a very simplified explanation of the signup and login process. It’s important to note that our code is not protected against timing attacks and it doesn’t use PKI infrastructure to check hashes, so there are plenty of vulnerabilities for hackers to exploit.
Cryptography itself can be described as the constant war between hackers and cryptographic engineers. Or, that familiar legal battle with your ex-wife over her maintenance payments. After all, what works today may not work tomorrow. A proof of MD5 hash algorithm vulnerability is a very good example.
So if your task is to ensure your users’ data privacy, be ready to constantly update your functions to counteract the recent ‘breakthroughs’.


What is password hashing and salting?
Introduction
Let's imagine that you decided to google ‘best sauces for Wagyu steak’. You went through several web pages, and then on page two of the search results, you get this notification from your Chrome browser:
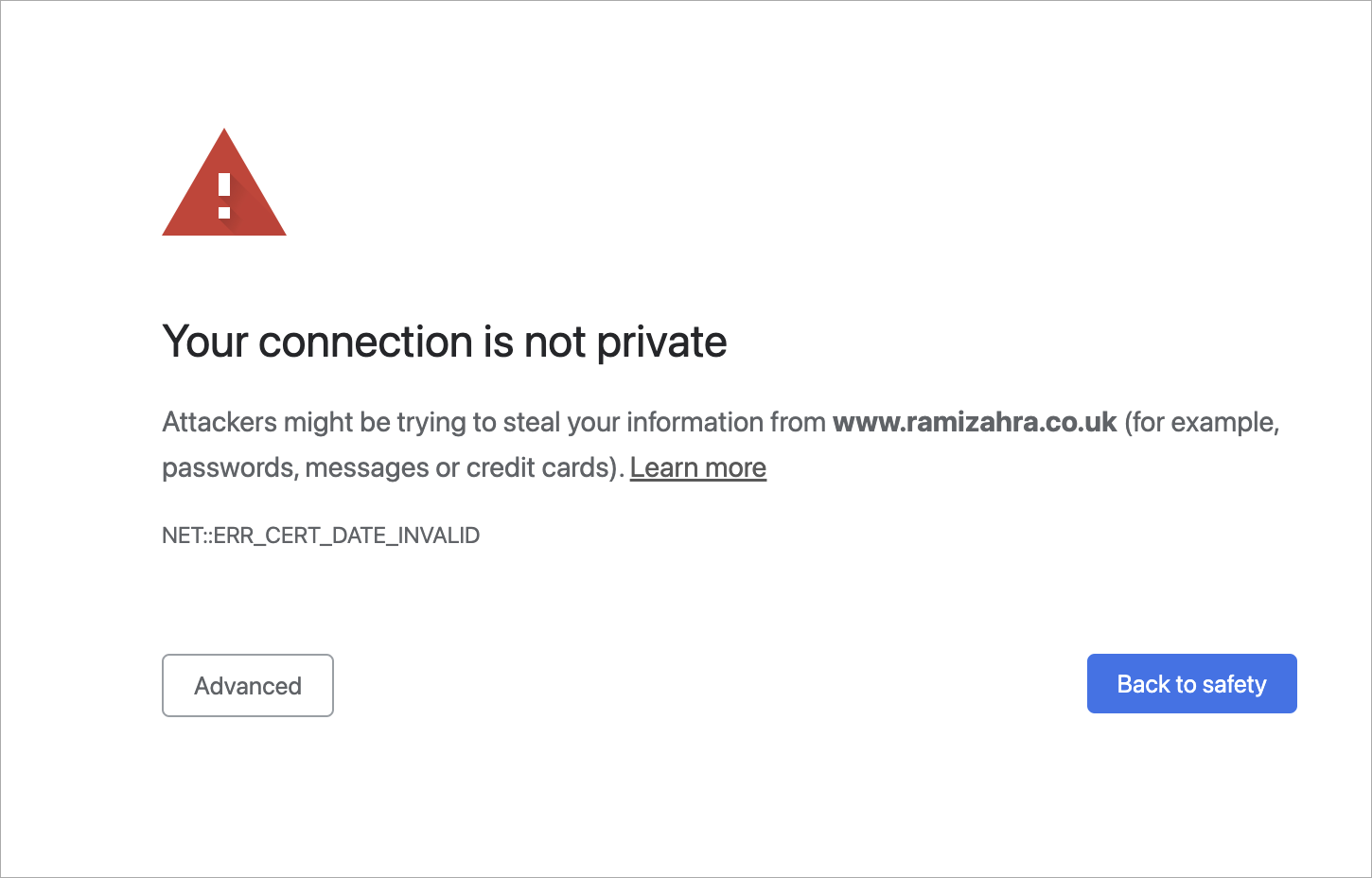
Something went wrong, that's for sure. What happened? Should you proceed to the page without a private connection?
An IT expert would surely reply:
The error that you got here was probably because of an SSL/TLS handshake failure.
SSL? TLS?? Acronyms you’ve no doubt heard before, but ones that nevertheless evoke a dreary sense of confusion in the untrained mind. In this article, we’ll try to explain what SSL/TLS is, how it works and at the very least, you’ll understand what that lock icon on the address bar is.
Where did TLS originate?
TLS stands for Transport Layer Security, and it is right now the most common kind of Web PKI. It’s used not only to encrypt internet browsing but also for end-to-end connection (video calling, messaging, gaming, etc.).
As for now, we expect almost any kind of connection on the internet to be encrypted, and if something is encrypted, we get an alert similar to that seen in figure A. But that wasn't always the case. If you go back to the mid-90s – very little on the internet was encrypted. Maybe that was because fewer people were using the internet back then, or maybe it was because there weren’t credit-card details flying all over the place.
The history of TLS starts with Netscape. In 1994, it developed Secure Socket Layer 1 – the grandfather of modern TLS. Technically, it fits between TCP and HTTP as a security layer. While version 1 was used only internally and was full of bugs, very quickly, they fixed all the issues and released SSL 2. Then, Netscape patented it in 1995 with a view to stopping other people patenting it so they could release it for free. This was a very odd yet generous move, considering what the real-life patent practice was at that time.
In 1995, the world was introduced to Internet Explorer, a browser that used a rival technology called PCT (Private Communications Technology), which was very similar to SSL. But as with any rivalry – there could only be one winner. In November 1996, SSL 3 was released, which, of course, was an improvement on SSL 2. Right after that, the Internet Engineering Task Force created the Transport Layer Security Working Group to decide what the new standard for internet encryption would be. It was subsequently renamed from SSL to TLS (as far as we know, this was because Microsoft didn't want Netscape to have dibs on the name). It actually took three years for the group to release TLS 1. It was so similar to SSL 3 that people began to name it SSL 3.1. But over time, through updates, the security level rose massively; bugs were terminated, ciphers were improved, protocols were updated etc.
How does TLS actually work?
TLS is a PKI protocol that exists between two parties. They effectively have to agree on certain things to identify each other as trustworthy. This process of identification is called a 'handshake'.
Let’s take a look at a TLS 1.2 handshake, as an example.
First, let's load any webpage, then, depending on your browser, press the lock icon near the web address text field. You’ll be shown certificate info and somewhere between the lines you'll find a string like this:
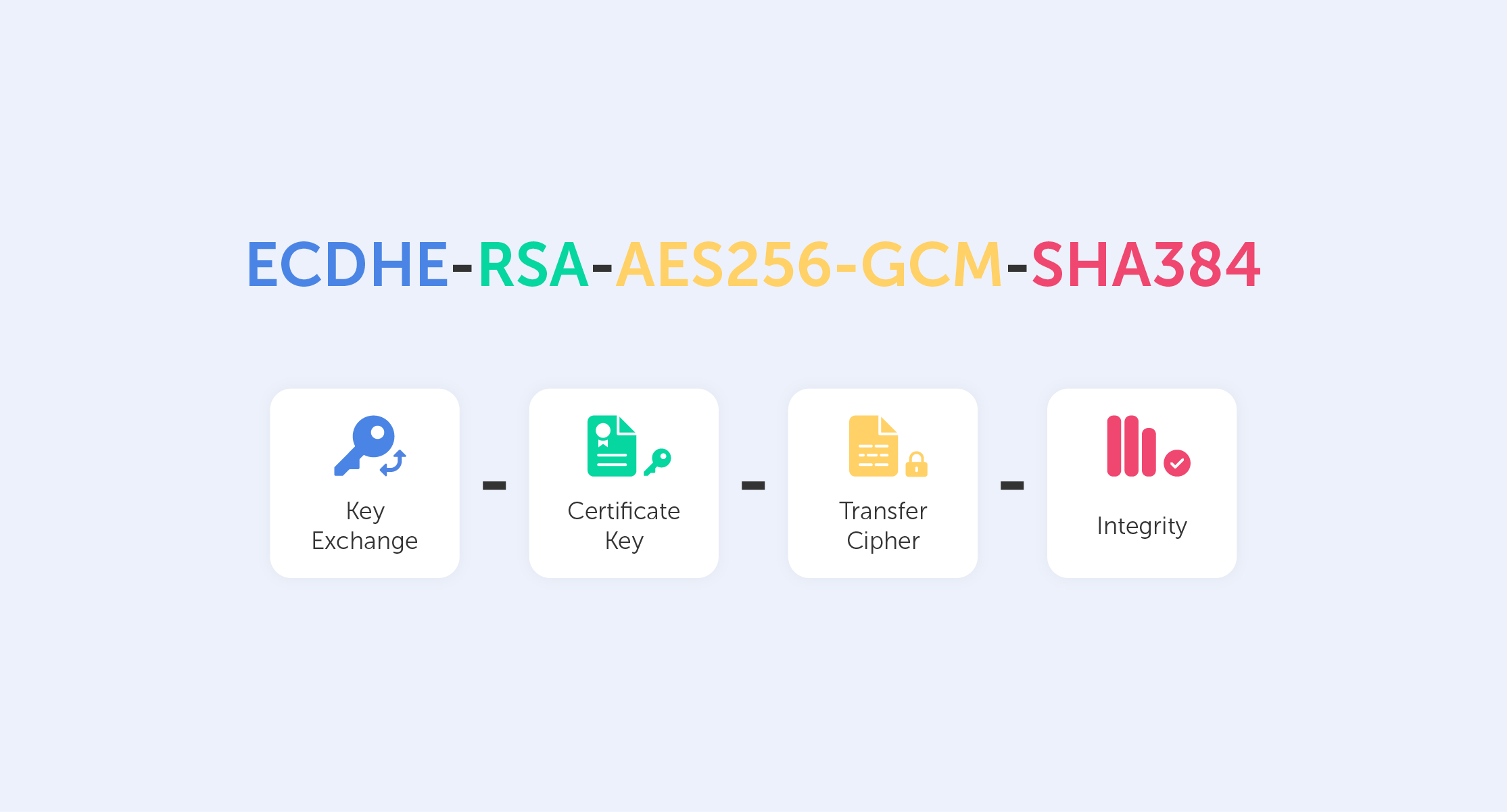
This is called a Cipher Suite. It’s a string-like representation of our 'handshake' recipe.
So, let’s go through some of the things shown here:
- First, we have ECDHE (Elliptic-curve Diffie–Hellman), which is a key agreement protocol that allows two parties, each having an elliptic-curve public–private key pair, to establish a shared secret over an insecure channel. In layman’s terms, this is known as key exchange;
- The RSA is our Public Key authentication mechanism (remember, we need a Public Key for any PKI);
- AES256 refers to the cipher that we’re going to use (AES) and its' key size (256);
- Lastly, SHA384 is effectively a building block that is used to perform hash functions.
Now, the trick is to exchange all that data in just several messages via our 'handshake'.
What exactly happens when we go to a new web page?
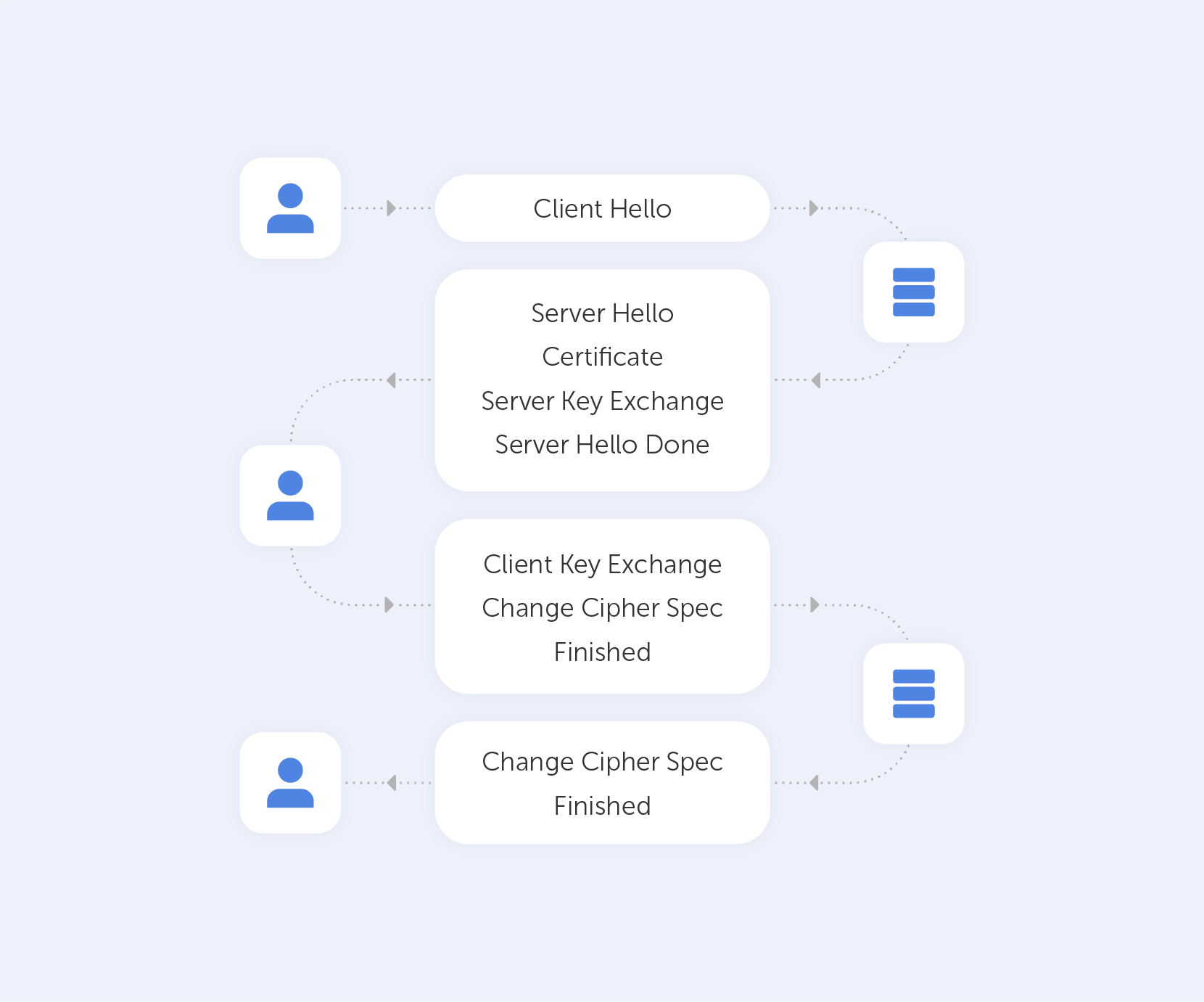
After we establish a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection, we start our handshake. As always on the web, the user (Client) is requesting data from the Server – so he sends a 'Client Hello' message, which contains a bunch of data including:
- The max TLS version that this Client can support so that both parties are able to 'speak the same language;
- A random number to protect from replay attacks;
- List of the cipher suites that the Client supports.
Assuming the Server is live, it responds with 'Server Hello', containing the Cipher Suite and TLS version it chose to connect with the Client + a random number. If the server can't choose a Suite or TLS version due to version incompatibility – it sends back a TLS Alert with a handshake failure. At this point, both the User and the Server know the communication protocol.
Keep in mind that the server is sending a Public key and a Certificate containing an RSA key. It’s important to know that the Certificate has an expiration date. You’ll understand why by the end of the article.
On top of that, the Server is sending a Server Key Exchange Message containing parameters for ECDHE with a public value. Very importantly, this Exchange Message also contains a digital signature (all previous messages are summarized using a hash function and signed using the private key of the Server). This signature is crucial because it provides proof that the Server is who they say they are.
When the Server is done transmitting all the above-mentioned messages, it sends a 'Server Hello Done' message. In Layman’s terms, that’s an ‘I’m done for the day, I’ll see you at the pub’ kind of message.
The Client, on the other hand, will look at the Certificate and verify it. After that, it will verify the signature using the Certificate (you can't have one without the other). If all goes well, the Client is assured of the Server’s authenticity and sends a Client Key Exchange Message. This message doesn't contain a Certificate but does contain a Premaster Secret. It is then combined with the random numbers that were generated during the ‘Hello’ messages to produce a Master Secret. The Master Secret is going to be used for encryption at the next step.
It may seem very complicated now, but we’re almost done!
The next stage involves the Client sending the ‘Change Cipher Spec’ message, which basically says "I’ve got everything, so I can begin encryption – the next message I'll send you is going to be encrypted with parameters and keys".
After that, the Client proceeds to send the ‘Finished’ message containing a summary of all the messages so far encrypted. This helps to ensure that nobody fiddled with the messages; if the Server can't decrypt the message, it leaves the 'conversation'.
The Server will reply in the same way – with a Change Cipher Spec and a Finished message.
Handshaking is now done, parties can exchange HTTP requests/responses and load data. By the way, the only difference between HTTP and HTTPS is that the last one is secure – that's what the 'S' stands for there.
As you can see, it's incredibly difficult to crack this system open. However, that's exactly what we need to ensure security. Moreover, those two round trips that the data travels take no time at all, which is great; nobody wants their GitHub to take a month and a half to load up. By the way, the more advanced TLS 1.3 does all that in just one round trip!
Your connection is not private
When something goes wrong with TLS, you’ll see the warning that we demonstrated at the very beginning of this article. Usually, those are issues associated with the Certificate and its expiration date. That’s why your internet will refuse to work if you’ve messed around with the time and date settings on your device. But, if everything with the date and time is in check – never proceed to a website that triggers this warning, because most likely, between you and the server, somebody is parsing your private data.



What is Transport Layer Security (TLS) & how does it work?
Let’s imagine that somehow you’re in the driver’s seat of a start-up, and a successful one too. You’ve successfully passed several investment rounds and you’re well on your way to success. Now, big resources lead to big data and with big data, there’s a lot of responsibility. Managing data in such a company is a struggle, especially considering that data is usually structured in an access hierarchy – Excel tables and Google Docs just don’t cut the cake anymore. Instead, the company yearns for a protocol well equipped to manage data. The company yearns for LDAP.
What is LDAP?
The story of LDAP starts at the University of Michigan in the early 1990s when a graduate student, Tim Howes, was tasked with creating a campus-wide directory using the X.500 computer networking standard. Unfortunately, accessing X.500 records was impossible without a dedicated server. Additionally, there was no such thing as a ‘client app’. As a result, Howes co-created DIXIE, a directory client for X.500. This work set the foundations for LDAP, a standards-based version of DIXIE for both clients and servers – an acronym for the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.
It was designed to maintain a data hierarchy for small bits of information. Unlike ‘Finder’ on your Mac, or ‘Windows Explorer’ on your PC, the ‘files’ inside the directory tree, although small, are contained in a very hierarchical order – exactly what you need to organize, for example, your HR structure, or when accessing a file. Compared to good old Excel, it is not a program, but rather a protocol. Essentially, a set of tools that allow users to find the information that they need very quickly.
Importantly, this protocol answers three key questions regarding data management:
— Who? Users must authenticate themselves in order to access directories.
— How? A special language is used that provides for query or data manipulations.
— Where? Data is stored and organized in a proper manner.
Let’s now go through these key questions in greater detail.
Who?
It’s bad taste to provide internal data to any old Joe. That’s why LDAP users cannot access information without first proving their identity.
LDAP authentication involves verifying provided usernames and passwords by connecting with a directory service that uses the LDAP protocol. All this data is stored in what is referred to as a core user. This is a lot like logging into Facebook, where you’re only able to access a user’s feed and photos if they’ve accepted your friend request, or if their profile has been set to public.
Some companies that require advanced security use a Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL), for example, Kerberos, for the authentication process.
In addition, to ensure the maximum safety of LDAP messages, as soon as data is accessed via devices outside the company’s walls, Transport Layer Security (TLS) may be used.
How?
The main task of a data management system is to provide “many things to many users”.
Rather than creating a complex system for each type of information service, LDAP provides a handful of common APIs (LDAP commands) to do this. Supporting applications, of course, have to be written to use these APIs properly. Still, the LDAP provides the basic service of locating information and can thus be used to store information for other system services, such as DNS, DHCP, etc.
Basic LDAP commands
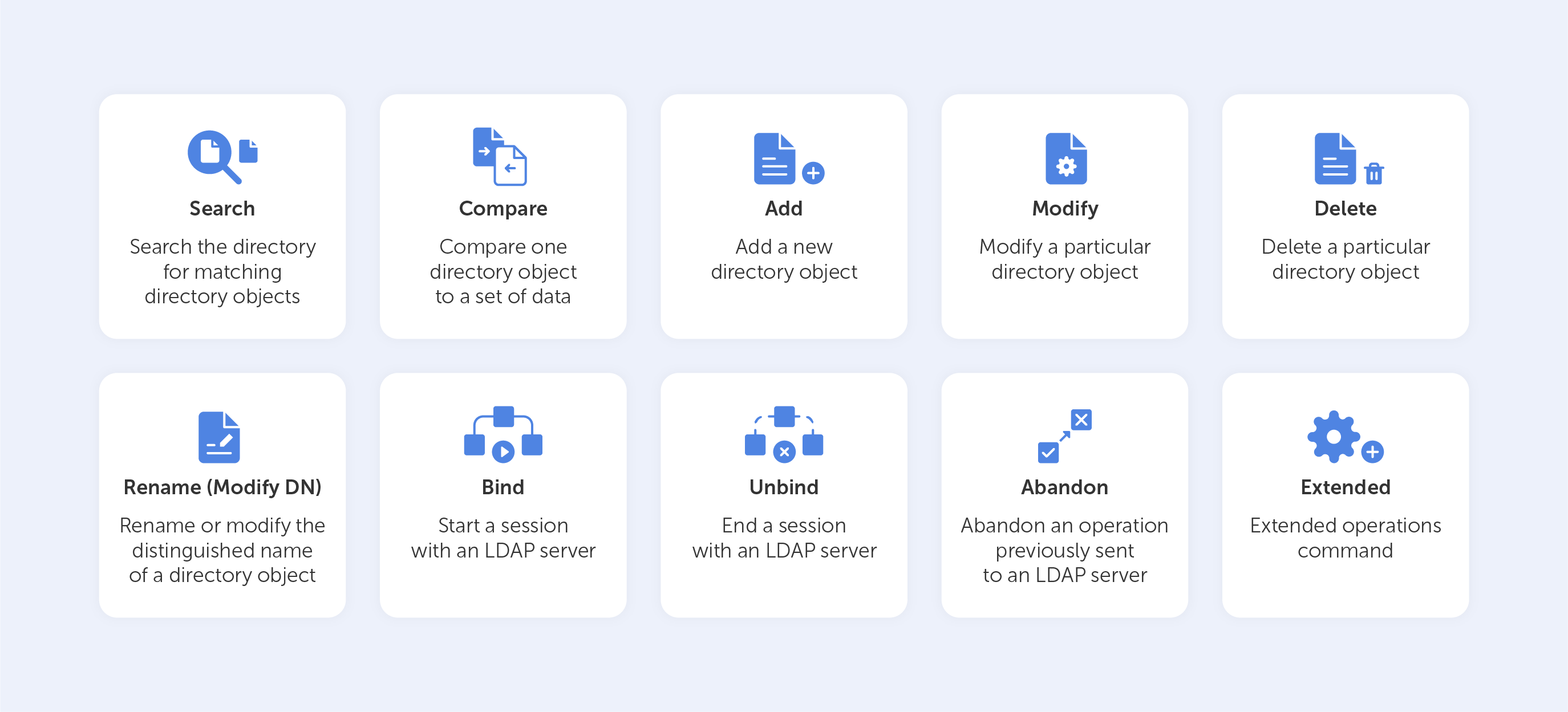
Let’s look at the ‘Search’ LDAP command as an example, if you’d like to know which group a particular user is a part of, you might need to input something like this:
(&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName=BradleyC)
(memberof=CN=Perohouse,OU=Users,DC=perohouse,DC=com))
Isn’t it beautiful? Not quite as simple as performing a Google search, that’s for sure. So, your employees will perform all their directory services tasks through a point-and-click management interface like Varonis DatAdvantage.
All those interfaces may vary depending on their configuration, which is why new employees should be trained to use them, even if they’ve used LDAP before.
Where?
As we mentioned before, LDAP has the structure of a tree of information. Starting with the roots, it contains hierarchical nodes relating to a variety of data, by which the query may then be answered.
The root node of the tree doesn't really exist and can't be accessed directly. There is a special entry called the root directory specific entry, or rootDSE, that contains a description of the whole tree, its layout, and its contents. But, this really isn't the root of the tree itself. Each entry contains a set of properties, or attributes, in which data values are stored.
The tree itself is called the directory information tree (DIT). Branches of this tree contain all the data on the LDAP server. Every branch leads to a leaf in the end – a data entry, or directory service entry (DSE). These entries contain actual records that describe objects such as users, computers, settings, etc.
For example, such a tree for your company could start with the description of a position held, starting with you at the top as the director, finishing at the bottom with Joe Bloggs, the intern.
Each position would be tied to a person with a set of attributes, complete with links to subordinates. The attributes for a person may include their name, surname, phone number, email, in addition to their responsibilities. Each attribute would have a value inside, like ‘Joe’ for name and ‘Bloggs’ for surname.
The actual data contents may vary, as they totally depend on use. For example, you could have data issuing rights to certain people regarding the coffee machine. So, no Frappuccino for our intern Joe.
Sure, you can add more sophisticated data regarding each individual – their personal family trees, or even voice samples for instance, but typically, the LDAP would just point to the place where such data can be found.
Is it worth it?
LDAP is able to aggregate information from different sources, making it easier for an enterprise to manage information. But as with any type of data organization, the biggest difficulty is creating a proper design for your tree. There is always trial and error involved while building a directory for a specific corporate structure. Sometimes this process is so difficult that it even results in the reorganization of the company itself in favor of the hierarchical model. Despite this, for almost thirty years, the LDAP has held its title as the most efficient solution for the organization of corporate data.



What is LDAP and how does LDAP authentication work?
Imagine you’re a system administrator at Home Depot. Just as you’re about to head home, you notice that your network has just authorized the connection of a new air-conditioner. Nothing too peculiar, right? The next morning, you wake up to find that terabytes of data including logins, passwords and customer credit card information have been transferred to hackers. Well, that’s exactly what happened in 2014, when a group of hackers, under the guise of an unassuming HVAC system, landed an attack that cost Home Depot over $17.5 million dollars, all over an incorrectly configured PKI. In this article, we’ll be conducting a crash course in PKI management.
So, what’s a PKI?
‘Public key infrastructure’ is a term that relates to a set of measures and policies that allow one to deploy and manage one of the most common forms of online encryption – public-key encryption. Apart from being a key-keeper for your browser, the PKI also secures a variety of different infrastructures, including internal communication within organizations, Internet of Things (IoT), peer to peer connection, and so on. There are two main types of PKIs:
• The Web PKI, also known as the “Internet PKI”, has been defined by RFC 5280 and refined by the CA/Browser Forum. It works by default with browsers and pretty much everything else that uses TLS (you probably use it every day).
• An Internal PKI – is the one you run for your own needs. We’re talking about encrypted local networks, data containers, enterprise IT applications or corporate endpoints like laptops and phones. Generally speaking, it can be used for anything that you want to identify.
At its core, PKI has a public cryptographic key that is used not to encrypt your data, but rather to authenticate the identities of the communicating parties. It’s like the bouncer outside an up-market club in Mayfair – you’re not getting in if you’re not on the list. However, without this ‘bouncer’, the concept of trustworthy online communication would be thrown to the wind.
So, how does it work?
PKI is built around two main concepts – keys and certificates. As with an Enigma machine, where the machine’s settings are used to encrypt a message (or establish a secure protocol), a key within a PKI is a long string of bits used to encrypt or decrypt encoded data. The main difference between the Enigma machine and a PKI is that with the latter, you have to somehow let your recipient know the settings used to encode the encrypted message.
The PKI gets its name because each party in a secured connection has two keys: public and private. A generic cipher protocol on the other hand, usually only uses a private one.
The public key is known to everyone and is used throughout the network to encode data, but the data cannot be accessed without a private key, which is used for decoding. These two keys are bound by complex mathematical functions which are difficult to reverse-engineer or crack by brute force. By the way, this principle is an epitome of asymmetrical cryptography.
So, this is how data is encrypted within a public key infrastructure. But let’s not forget that identity verification is just as important when dealing with PKIs – that’s where certificates come into play.
Digital Identity
PKI certificates are most commonly seen as digital passports containing lots of assigned data. One of the most important pieces of information in such a certificate relates to the public key: the certificate is the mechanism by which that key is shared – just like your Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) or driver’s license, for instance.
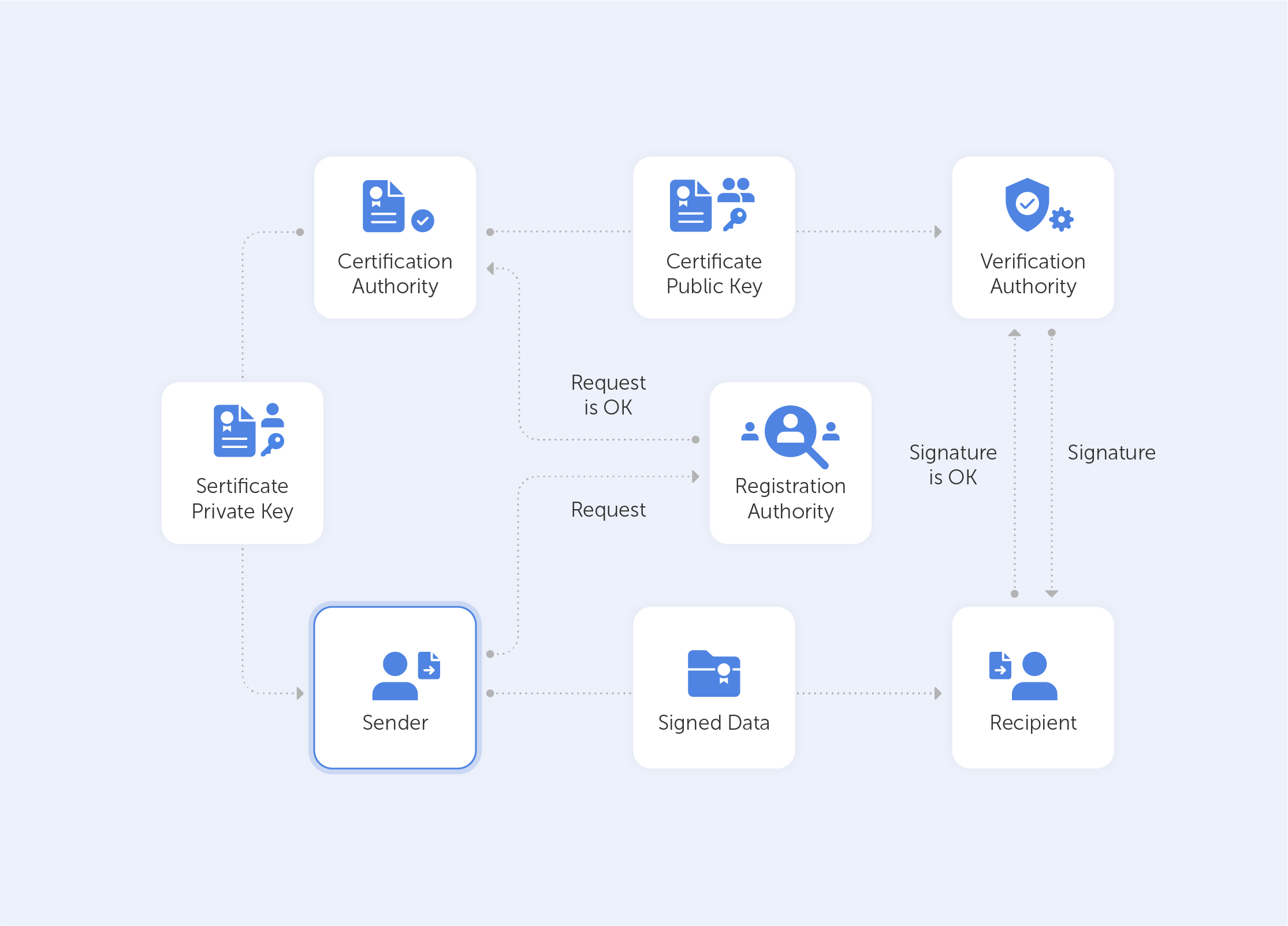
But it’s not really valid unless it has been issued by some kind of entrusted authority. In our case, this is the certificate authority (CA). Here, there is an attestation from a trusted source that the entity is who they claim to be.
With this in mind, it becomes very easy to grasp what the PKI consists of:
• A certificate authority, which issues digital certificates, signs them with its public key and stores them in a repository for reference;
• A registration authority, which verifies the identities of those requesting digital certificates. A CA can act as its registration authority or can use a third party to do so;
• A certificate database that stores both the certificates, their metadata and, most importantly, their expiration dates;
• A certificate policy outlining the PKI's procedures (this is basically a set of instructions that allows others to judge how trustworthy a PKI is).
What is a PKI used for?
A PKI is great for securing web traffic – data flowing through the open internet can be easily intercepted and read if it isn't encrypted. Moreover, it can be difficult to trust a sender’s identity if there isn’t some kind of verification procedure in place.
But even though SSL/TLS certificates (that secure browsing activities) may demonstrate the most widespread implementation of PKI, the list doesn’t end there. PKI can also be used for:
• Digital signatures on software;
• Restricted access to enterprise intranets and VPNs;
• Password-free Wi-fi access based on device ownership;
• Email and data encryption procedures.
PKI use is taking off exponentially; even a microwave can connect to Instagram nowadays. This emerging world of IoT devices brings us new challenges and even devices seemingly existing in closed environments now require security. Taking the ‘evil air conditioner’ that we spoke about in the introduction as an example – gone are the days where we can take a piece of kit for face value. Some of the most compelling PKI use cases today center around IoT. Auto manufacturers and medical device manufacturers are two prime examples of industries currently introducing PKI for IoT devices. Edison’s Electronic Health Check-up System would be a very good example here, but we’ll save that for a future deep-dive.
Is PKI a cure-all?
As with any technology – execution is sometimes more important than the design itself. A recent study by the Ponemon Institute surveyed nearly 603 IT and security professionals across 14 industries to understand the current state of PKI and digital certificate management practices. This study revealed widespread gaps and challenges, for example:
• 73% of security professionals admit that digital certificates still cause unplanned downtime and application outages;
• 71% of security professionals state that migration to the cloud demands significant changes to their PKI practices;
• 76% of security professionals say that failure to secure keys and certificates undermines the trust their organization relies upon to operate.
The biggest issue, however, is that most organizations lack the resources to support PKI. Moreover, only 38% of respondents claim they have the staff to properly maintain PKI. So for most organizations PKI maintenance becomes a burden rather than a cure-all.
To sum up, PKI is a silent guard that secures the privacy of ordinary online content consumers. However, in the hands of true professionals, it becomes a power tool that creates an encryption infrastructure that is almost infinitely scalable. It lives in your browser, your phone, your Wi-fi access point, throughout the web and beyond. Most importantly, however, a correctly-configured PKI is the distance between your business and an imposter air conditioner that wants your hard-earned cash.


What is PKI? A Public Key Infrastructure definitive guide

Why password managers matter and how they work
Password managers are a game-changer when it comes to security, convenience and efficiency. If you're new to them, you might be wondering what is the purpose of a password manager? The answer lies in avoiding the risks that come with weak or reused passwords. Managing passwords securely can be a real challenge. Cyber threats like identity theft, data breaches and more are all too real. The safest way to store passwords is with a personal password keeper.
Think of it as a simple password vault for all your login credentials. Rather than relying on your memory or insecure methods like writing them down, the safest place to keep passwords is using a password manager ensuring that all your credentials are stored in an encrypted database, accessible only through a master password. With a password manager, you can secure your password and create strong, unique passwords — no more worrying about remembering them all.
What do password managers do? They securely store passwords, and many also help in automatically filling in your credentials on websites, reducing the risk of phishing attacks. They also help with keeping passwords securely across all your devices — that means your credentials are safe wherever you access them.
Why a password manager is essential for security
The human factor in digital security
The more digital we become — the COVID-19 pandemic has certainly accelerated that — the more online accounts we have. And with that comes more passwords to keep track of. Unfortunately, human error is a leading cause of data breaches. People still use weak passwords or reuse the same credentials across multiple sites. That makes it far too easy for cybercriminals to get in. Password managers enhance your password practices to prevent vulnerabilities.
Phishing attacks have become incredibly common, and weak password practices expose businesses to risks. Is it safe to use password managers? Yes, a password manager eliminates the risk of human error and keeps your credentials safe by storing them in an encrypted database. It can automatically fill in your credentials only when a legitimate site is detected. That stops you from unknowingly entering passwords on phishing sites. And because it eliminates the risk of human error, protecting your passwords becomes much easier.
Security audits
Security audits are a key part of any business's security strategy. Weak, outdated, or compromised credentials can lead to security vulnerabilities. Businesses that fail to enforce strong password policies risk non-compliance with industry regulations.
One of the key benefits of password managers is that it can automatically alert users when passwords need updating. It also provides an audit trail, making it easier to track and manage password changes efficiently. Additionally, password managers ensure quick password rotation when an employee leaves the company, minimizing the risk of data leaks — this proactive security measure helps companies comply with industry standards and pass audits with ease.
Managing absences and staff changes
Temporary absences and staff turnover can disrupt business workflows. A business password manager ensures employees with the necessary permissions can access credentials securely. That prevents bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
For example, if a key team member is on vacation or out sick, other employees may need access to shared accounts. With a password manager, authorized team members can securely retrieve credentials without compromising security.
Disaster recovery is another critical aspect. In the unfortunate event of an emergency where key personnel are unavailable, having a secure and structured password management system ensures continuity. Companies can avoid business disruptions by ensuring authorized personnel can access critical information without compromising security policies.
Seamless access across devices and browsers
A key advantage of password managers is that they work seamlessly across multiple browsers and devices. Solutions like Passwork are where flexibility really shines. Whether you’re using a desktop, laptop, or smartphone, you can securely store your passwords and access them anywhere. That's especially useful for remote teams, who need smooth and secure login experiences.
Browser extensions fill in credentials automatically, cutting down on login friction. You can use Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Edge — your choice. Many password managers support cross-platform synchronization, changes made on one device are instantly available on another.
Password manager pricing and what to expect
Password managers come in all shapes and sizes, and so do the costs. You can get a basic version for free, with the essentials, while premium plans offer advanced security features like two-factor authentication, encrypted password sharing and audit logs. Choosing an easy to use password manager is essential for keeping things simple and secure. Business solutions often include features for multiple users, ensuring secure credential management across the board.
While a free password manager may be sufficient for individuals, businesses should consider paid options to benefit from enterprise-grade security and administrative controls. Scalable plans that grow with your organization's needs can be a cost-effective way to manage security. And the cost of investing in a password manager is often much lower than the financial and reputational damage caused by a data breach.
Organizations that proactively invest in password security mitigate risks and reduce the likelihood of costly security incidents. When you're shopping for the best way to store passwords, consider what matters most to you: encryption, ease of use, and the ability to store passwords securely across different platforms. Look for features like two-factor authentication and secure password sharing for optimal protection.
Getting started with a password manager
How to use a password manager? It’s pretty straightforward — choose a password manager that fits your needs. Consider factors such as encryption strength, compatibility with devices, and business-oriented features if you need them.
- Install the software or use a web-based version for cloud-based access
- Create a strong master password that will grant access to all your stored credentials
- Start storing passwords securely by importing existing credentials or generating new, strong passwords
- Enable auto-fill and auto-change to save time and reduce the risk of phishing attacks
- Set up two-factor authentication (2FA) for extra security layer against unauthorized access
Password managers also allow users to categorize passwords into folders or groups, making it easier to manage credentials efficiently. Businesses can take advantage of role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure employees only have access to the passwords relevant to their job responsibilities.
Different types of password managers
Cloud-based
Cloud-based solutions store encrypted passwords on remote servers, allowing you to access your credentials from any device. They offer convenience and accessibility, but you have to trust the provider's security measures. Passwork Cloud ensures high-level encryption and secure access, giving businesses full control over their password management while maintaining ease of use.
Self-hosted
Self-hosted solutions store passwords on a company servers rather than the cloud. While they reduce the risk of cloud-based attacks. Self-hosted password managers provide organizations with complete data control, allowing them to implement their own security policies and compliance measures. This makes them ideal for companies that prioritize on-premises data security.
Browser-based
Many web browsers offer built-in password management tools, but they often lack the advanced security features of dedicated solutions. Web browser password manager is better suited for casual users rather than businesses handling sensitive data. These managers may also be vulnerable to browser-based threats or device compromises. A standalone password manager is a more robust choice for organizations that require enterprise-grade security.
Essential features of a reliable password manager
Strong encryption
A secure password manager should use AES-256 encryption to protect stored credentials from cyber threats. This ensures that even if your data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized users.
Auto-fill and auto-change
These features simplify login processes and improve password security by automatically updating passwords when needed. Auto-change is particularly useful for regularly updating credentials without manual effort.
Two-factor authentication
Adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that even if a master password is compromised, unauthorized access is prevented. Many password managers support biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, for added protection.
Intuitive and user-friendly interface
A password manager should be easy to navigate, making it simple for users to store, retrieve, and manage credentials effectively.
Stay safe and secure your data with a password manager
Secure password management is a must. If you haven't started using a password manager yet, now is the time to take control of your online security. If you use a password manager what do you as the user need to remember is just a single master password — that's it. Protect your passwords with the help of a password manager and keep them safe from cyber threats.
Passwork is where security and convenience meet-the necessities for businesses that are serious about staying ahead. That means more than just a password manager. It means a robust security system that reduces the risk of human error. By automating password management and giving you secure, centralized access to sensitive data Passwork helps you protect your business in real-time.
Whatever your company size, investing in secure password management just makes sense. Don't wait for a data breach to happen. Take the next step now with Passwork and start protecting what matters most.



Why do I need a password manager?
Password managers protect your accounts by encrypting credentials, generating strong passwords, and blocking phishing attacks. They help individuals and businesses streamline password management, minimizing risks from weak or reused passwords. Discover their key features in the full article.

A couple of guesses — your mother's maiden name, your date of birth, your pet's name. And Bam! Your password is stolen.
Password theft is becoming more common every day. While one of the most notorious incidents was the 2014 Russian hacker incident that compromised more than 1.2 billion passwords, this is far from an isolated event. There are news stories about password-related breaches almost every day. And yet, many people continue to use weak, easily guessable passwords.
Why? Because they’re easy to remember. But as simple as these passwords are for you, they’re even easier for hackers to crack. This is a serious concern for businesses, where cybersecurity is paramount.
Why security policies alone aren't enough
Large enterprises often implement password policies requiring employees to use strong passwords. However, since it's easier to remember short passwords, many employees disregard the policies and choose weak passwords. A policy alone isn’t much help here.
The solution? A corporate password manager that ensures strong, unguessable passwords are used across the company. By using the right technology, you can significantly reduce the risk of a data breach.
While a corporate password manager can choose passwords for you, how do you choose the right one for your business? Here are some tips to help you find the best software for your enterprise.
Tip #1: Choose the right solution for your company
Password management solutions typically come in two forms: SaaS (cloud-based) or on-premise. Both have their advantages, depending on your company’s needs.
- SaaS (Software-as-a-Service): This option is managed by the provider, and you typically pay a subscription fee based on the number of users or the level of service. SaaS solutions are great for small- to mid-sized businesses, as they offer flexibility, scalability, and minimal setup costs.
- On-Premise: With an on-premise solution, the software is hosted on your company’s own servers. While there’s a higher upfront cost for hardware and software licenses, this option is ideal for larger enterprises that require full control over their data for compliance or security reasons.
Both options have their merits, so choose a vendor that offers both SaaS and on-premise solutions. This way, you can make a decision based on your company’s specific needs, ensuring you have the right balance between cost, security, and scalability.
Tip #2: Identify potential vulnerabilities
A critical feature of any corporate password manager is its ability to safeguard your data against vulnerabilities. Before committing to a solution, take the time to identify any weak points in the software.
Here’s a quick test: Sign in to the password manager and press F12 to open the browser’s developer console. In the “Network” tab, check for any external requests, like analytics scripts or third-party integrations. A secure password manager should not allow external third-party scripts that could expose you to cross-site scripting (XSS) or other attacks.
When third parties are allowed to call into the system, they can make the system vulnerable. Whether you prefer a SaaS password manager or an on-premise password manager, it should hold all sensitive information in such a way that external applications cannot access them.
Tip #3: Verify encryption standards
The password manager should store all passwords in an encrypted form. To verify this, use the browser’s developer tools again (F12 → Network tab). Now open any website where you need to sign in. Save the password in the password manager. Check whether the password appears as plain text or in encrypted form.
If it’s stored in plain text, the system is vulnerable to hacks. Strong encryption is essential. Look for password managers that use AES-256 encryption combined with an RSA handshake, which is the gold standard for secure data encryption.
Different password managers have different encryption standards. The highest cipher is AES-256 with an RSA handshake. This is military-grade encryption and is virtually unhackable. If your corporate password manager provides this level of encryption and owns its own servers, you don’t have to worry about the security of your information.
Tip #4: Choose a vendor with transparent policies
When selecting a password manager, transparency is key. Check the vendor’s website for whitepapers and documentation on the algorithms and cryptography they use. Vendors with open-source or auditable code are preferable, as they demonstrate a commitment to transparency and security.
Zero-knowledge encryption is another critical feature. This means that the vendor has no access to your master password or any of your sensitive data. For instance, Passwork ensures all passwords are stored in encrypted vaults using a 256-bit cipher, making them accessible only to the user.
Opting for an open-source solution is a smart move, as it allows you to inspect the code and confirm that the cryptography being used is reliable and secure.
Tip #5: Ensure auditability
If you opt for an on-premise solution, auditability is important. You should be able to inspect and audit the internal code to verify that it meets your company’s security standards.
Regular password audits are also essential for maintaining a secure system. A good password manager will automatically notify you when passwords need to be updated due to age or reuse across multiple services. This feature helps maintain optimal security across your entire organization.
If the code is open-source, you may even have the ability to customize it. However, be cautious, as making changes to the code can introduce instability. Always consult with the vendor before making any significant modifications.
Tip #6: Implement two-factor authentication (2FA)
A reliable corporate password manager should support strong two-factor authentication (2FA) options to enhance security. Passwords alone aren’t always enough to safeguard sensitive data, as they can be stolen or cracked. 2FA ensures that even if a password is compromised, an additional authentication factor—such as a code sent to your phone or an authentication app—protects your accounts.
When selecting a password manager, ensure it integrates with a variety of 2FA methods, such as time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) or SMS codes. Implementing 2FA will greatly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your corporate accounts, making it an essential security measure for any business.
Tip #7: Test the SSL security
Advanced corporate password management tools use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The SSL transfers data securely between the client and the server. Passwork uses SSL along with AES-256 bit encryption and RSA handshake to ensure your data is encrypted according to the highest standards.
There are several online tools to check if there are any potential issues with the SSL quality of the password manager. With tools such as SSL Labs and SSL Checker, you can find out if the SSL certificates of the password manager are valid.
Tip #8: Look for flexibility across platforms
A good corporate password manager should work seamlessly across all platforms and devices your employees use. Whether it’s desktop or mobile, macOS, Windows, iOS, or Android, the solution should offer compatibility with all major operating systems.
Additionally, ensure the password manager offers browser extensions for popular web browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Syncing across devices is another crucial feature. If an employee saves a password on their desktop browser, it should automatically be available when they log in on their mobile device.
The bottom line
There are several corporate password managers available, but make sure you choose the best one. Your password manager should not only be secure but also adaptable to your company’s needs. If you find a password manager that meets all the criteria listed above and is affordable, choose it to safeguard your passwords.
Remember, security isn’t an area where you can afford to cut corners. Your enterprise passwords are extremely important so don’t compromise on quality. Choose password manager that meets all your security requirements, including strong encryption, transparency, auditability, and two-factor authentication.
As the saying goes, “If you’re not paying for the product, you are the product.” Make the right choice by selecting software that keeps your company’s details safe. It not only simplifies things for your employees but also ensures your valuable information remains secure from prying eyes.





















